MASTG-TECH-0124: Achieving a MITM Position Using a Rogue Access Point
To achieve a Machine-in-the-Middle (MITM) position, you can set up a network where all traffic between the target mobile device and the external network is routed through your host computer. This can be done in one of two ways:
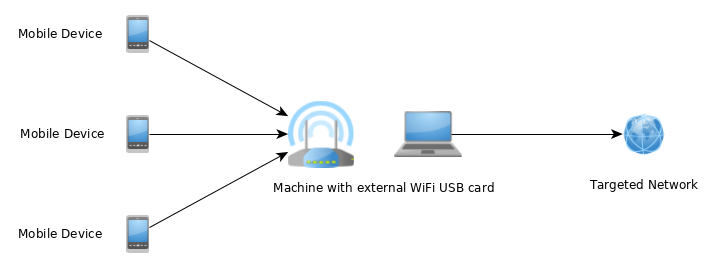
Option 1: Using an external access point: Both the mobile device and your host computer connect to a separate access point. This setup is useful for bypassing host isolation mechanisms in public or enterprise networks. Traffic from the mobile device is then redirected through your host for interception.
The scenario with a separate access point requires access to the configuration of the AP and you should check first if the AP supports either:
- port forwarding or
- has a span or mirror port.
Option 2: Your host as the access point: Your host computer itself acts as the access point, directly controlling network traffic. This can be configured in different ways: - Using your host's built-in WiFi card as the access point while connecting to the target network via a wired connection. - Using an external USB WiFi adapter as the access point while your built-in WiFi connects to the target network (or vice versa).
First, if you're going to use an external USB WiFi card, ensure that the card has the capability to create an access point. You can verify if your WiFi card has AP capabilities by using the command iwconfig on Kali Linux:
iw list | grep AP
In both cases the AP needs to be configured to point to your host computer's IP. Your host computer must be connected to the AP (via wired connection or WiFi) and you need to have connection to the target network (can be the same connection as to the AP). Some additional configuration may be required on your host computer to route traffic to the target network.
Installation¶
The following procedure is setting up a MITM position using an access point and an additional network interface:
Create a WiFi network either through a separate access point or through an external USB WiFi card or through the built-in card of your host computer.
This can be done by using the built-in utilities on macOS. You can use share the internet connection on Mac with other network users.
For all major Linux and Unix operating systems you need tools such as:
- hostapd
- dnsmasq
- iptables
- wpa_supplicant
- airmon-ng
For Kali Linux you can install these tools with apt-get:
apt-get update
apt-get install hostapd dnsmasq aircrack-ng
iptables and wpa_supplicant are installed by default on Kali Linux.
In case of a separate access point, route the traffic to your host computer. In case of an external USB WiFi card or built-in WiFi card the traffic is already available on your host computer.
Route the incoming traffic coming from the WiFi to the additional network interface where the traffic can reach the target network. Additional network interface can be wired connection or other WiFi card, depending on your setup.
Configuration¶
We focus on the configuration files for Kali Linux. Following values need to be defined:
- wlan1 - id of the AP network interface (with AP capabilities),
- wlan0 - id of the target network interface (this can be wired interface or other WiFi card)
- 10.0.0.0/24 - IP addresses and mask of AP network
The following configuration files need to be changed and adjusted accordingly:
-
hostapd.conf
# Name of the WiFi interface we use interface=wlan1 # Use the nl80211 driver driver=nl80211 hw_mode=g channel=6 wmm_enabled=1 macaddr_acl=0 auth_algs=1 ignore_broadcast_ssid=0 wpa=2 wpa_key_mgmt=WPA-PSK rsn_pairwise=CCMP # Name of the AP network ssid=STM-AP # Password of the AP network wpa_passphrase=password -
wpa_supplicant.conf
network={ ssid="NAME_OF_THE_TARGET_NETWORK" psk="PASSWORD_OF_THE_TARGET_NETWORK" } -
dnsmasq.conf
interface=wlan1 dhcp-range=10.0.0.10,10.0.0.250,12h dhcp-option=3,10.0.0.1 dhcp-option=6,10.0.0.1 server=8.8.8.8 log-queries log-dhcp listen-address=127.0.0.1
MITM Attack¶
To be able to get a MITM position you need to run the above configuration. This can be done by using the following commands on Kali Linux:
# check if other process is not using WiFi interfaces
$ airmon-ng check kill
# configure IP address of the AP network interface
$ ifconfig wlan1 10.0.0.1 up
# start access point
$ hostapd hostapd.conf
# connect the target network interface
$ wpa_supplicant -B -i wlan0 -c wpa_supplicant.conf
# run DNS server
$ dnsmasq -C dnsmasq.conf -d
# enable routing
$ echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
# iptables will NAT connections from AP network interface to the target network interface
$ iptables --flush
$ iptables --table nat --append POSTROUTING --out-interface wlan0 -j MASQUERADE
$ iptables --append FORWARD --in-interface wlan1 -j ACCEPT
$ iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -j MASQUERADE
Now you can connect your mobile devices to the access point.