MASTG-TECH-0123: Achieving a MITM Position via ARP Spoofing
When proxy-based interception fails due to non-HTTP protocols or non-proxy-aware apps, ARP Spoofing can be used to redirect network traffic. ARP Spoofing is a Layer 2 attack that allows an attacker to impersonate the network gateway, forcing the mobile device to send its traffic through the attacker's machine.
This technique works against any device and operating system as the attack is executed on OSI Layer 2. When you are MITM, you might not be able to see clear text data, as the data in transit might be encrypted by TLS, but it will give you valuable information about the hosts involved, the protocols used, and the ports the app is communicating with.
To execute an ARP Spoofing attack, you can use bettercap.
Important: Modern operating systems implement defenses such as encrypted DNS (DoH, DoT), MAC address randomization, and ARP spoofing detection, making this technique less effective on newer devices.
Network Setup¶
To achieve a Machine-in-the-Middle (MITM) position, your host computer must be on the same wireless network as the mobile device and the gateway it communicates with. Once this is set up, you need to obtain the IP address of the mobile device. For a complete dynamic analysis of a mobile app, all network traffic should be intercepted and analyzed.
MITM Attack¶
Start your preferred network analyzer tool first, then start bettercap with the following command and replace the IP address below (X.X.X.X) with the target you want to execute the MITM attack against.
$ sudo bettercap -eval "set arp.spoof.targets X.X.X.X; arp.spoof on; set arp.spoof.internal true; set arp.spoof.fullduplex true;"
bettercap v2.22 (built for darwin amd64 with go1.12.1) [type 'help' for a list of commands]
[19:21:39] [sys.log] [inf] arp.spoof enabling forwarding
[19:21:39] [sys.log] [inf] arp.spoof arp spoofer started, probing 1 targets.
bettercap will then automatically send the packets to the network gateway in the (wireless) network and you are able to sniff the traffic. Beginning of 2019 support for full duplex ARP spoofing was added to bettercap.
On the mobile phone start the browser and navigate to http://example.com, you should see output like the following when you are using Wireshark.
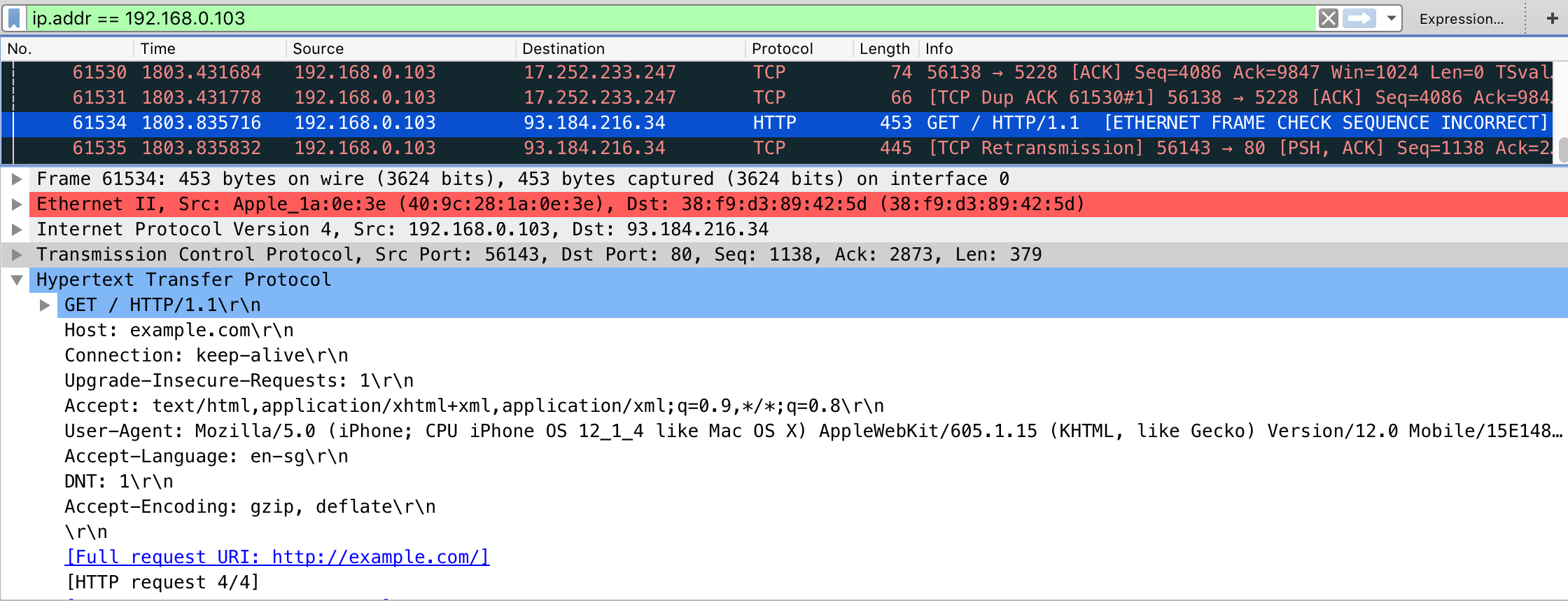
If that's the case, you are now able to see the complete network traffic that is sent and received by the mobile phone. This includes also DNS, DHCP and any other form of communication and can therefore be quite "noisy". You should therefore know how to use DisplayFilters in Wireshark or know how to filter in tcpdump to focus only on the relevant traffic for you.