MASTG-KNOW-0019: Deep Links
Deep links are URIs of any scheme that take users directly to specific content in an app. An app can set up deep links by adding intent filters on the Android Manifest and extracting data from incoming intents to navigate users to the correct activity.
Android supports two types of deep links:
- Custom URL Schemes, which are deep links that use any custom URL scheme, e.g.
myapp://(not verified by the OS). - Android App Links (Android 6.0 (API level 23) and higher), which are deep links that use the
http://andhttps://schemes and contain theautoVerifyattribute (which triggers OS verification).
Deep Link Collision:
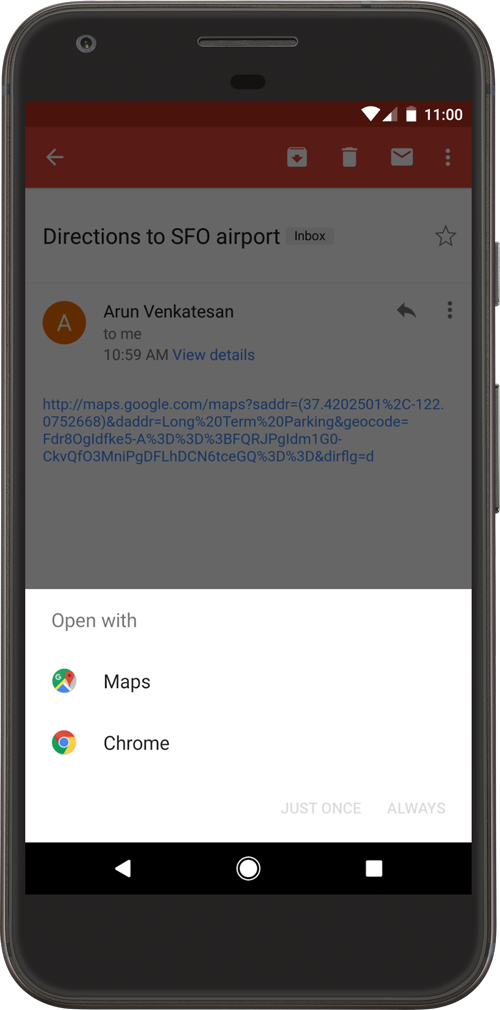
Using unverified deep links can cause a significant issue- any other apps installed on a user's device can declare and try to handle the same intent, which is known as deep link collision. Any arbitrary application can declare control over the exact same deep link belonging to another application.
In recent versions of Android this results in a so-called disambiguation dialog shown to the user that asks them to select the application that should handle the deep link. The user could make the mistake of choosing a malicious application instead of the legitimate one.
Android App Links:
In order to solve the deep link collision issue, Android 6.0 (API Level 23) introduced Android App Links, which are verified deep links based on a website URL explicitly registered by the developer. Clicking on an App Link will immediately open the app if it's installed.
There are some key differences from unverified deep links:
- App Links only use
http://andhttps://schemes, any other custom URL schemes are not allowed. - App Links require a live domain to serve a Digital Asset Links file via HTTPS.
- App Links do not suffer from deep link collision since they don't show a disambiguation dialog when a user opens them.